Why Beginners Fail in Agriculture and Cattle Farming in Nepal

Agriculture and cattle farming are vital to Nepal’s economy, yet many beginners entering these fields face significant challenges. One primary reason for failure is lack of experience and technical knowledge. Many new farmers underestimate the complexities of soil management, seasonal crop planning, disease prevention, and livestock care. Without proper training, they are unable to respond effectively to pests, market fluctuations, or animal health issues.
Another factor is limited access to capital and infrastructure. Beginners often start with small investments, but unexpected costs—such as veterinary services, feed shortages, or irrigation needs—can quickly overwhelm them. Poor road connectivity and inadequate cold storage facilities also make it difficult to sell products at fair prices, especially in remote areas.
Market instability further discourages new entrants. The price of agricultural products in Nepal can vary greatly within a short time. Farmers without strong networks or market awareness often sell at low prices or face product losses.
In cattle farming, feed management and animal health are major hurdles. Beginners may not have enough knowledge about balanced nutrition or disease prevention, leading to reduced productivity and high mortality rates.
Finally, social perception and lack of youth engagement play a role. Many young people view agriculture as less prestigious compared to urban jobs, leading to a shortage of innovative ideas in the sector.

Table 1: Interest of Youth Towards Agriculture (by Age Category)
Age Category | High Interest (%) | Moderate Interest (%) | Low Interest (%) |
15–20 | 30 | 40 | 30 |
21–25 | 25 | 35 | 40 |
26–30 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
31–35 | 15 | 25 | 60 |
Table 2: Categories of Agricultural Attraction in Nepal
Category | Attraction Level (%) |
Organic Farming | 40 |
Commercial Vegetable Production | 35 |
Fruit Orchards | 25 |
Dairy Farming | 50 |
Poultry Farming | 45 |
Fish Farming | 20 |
Herbal & Medicinal Plant Cultivation | 30 |
Pie Chart: Startups vs Failures in Agriculture and Cattle Farming
Successful Startups: 35%
Failures: 65%
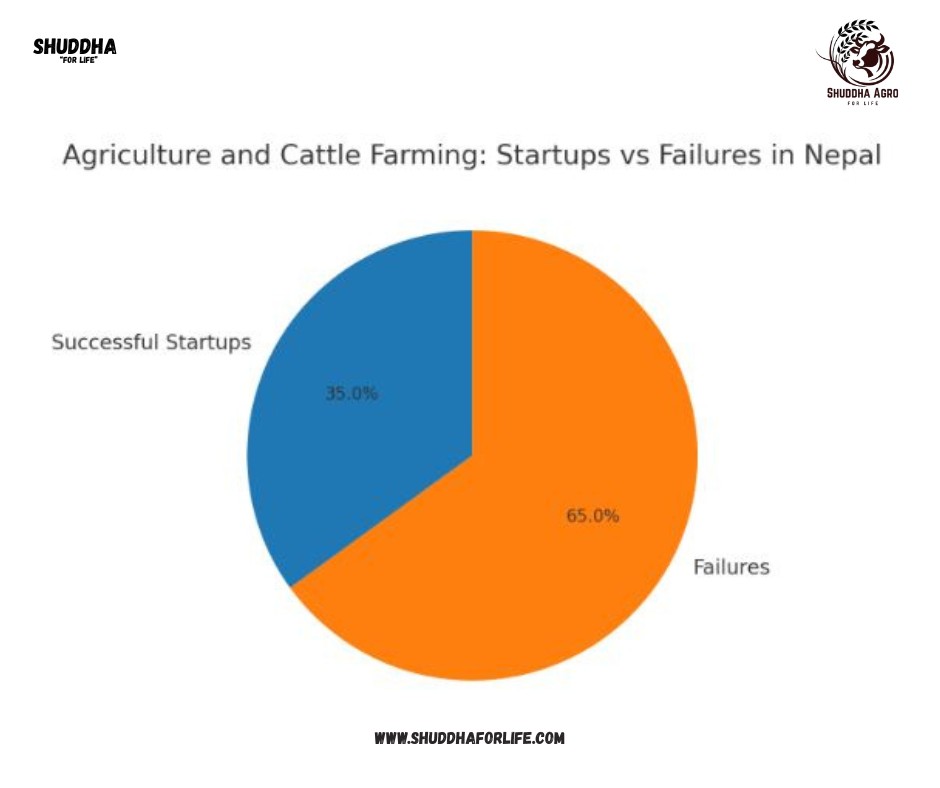
This indicates that nearly two-thirds of new ventures in agriculture and cattle farming in Nepal do not succeed, largely due to inexperience, lack of resources, and poor market connectivity.
Conclusion
Education equips farmers with scientific knowledge about soil, crops, and livestock. Experience helps them adapt to local challenges and market trends. Perseverance is crucial to withstand failures, learn from mistakes, and steadily improve. A combination of these three qualities—education, experience, and perseverance—is the cornerstone of long-term success in agriculture and cattle farming in Nepal.
Related Posts

12 Aug, 2025
Why Beginners Fail in Agriculture and Cattle Farming in Nepal
an article to show attraction practices and failure reasons
 HOME
HOME


